Ethane is a colorless, flammable gas with a sweet smell. It is the simplest alkane, and the main component of natural gas. Ethane is used as a starting material for many industrial processes, such as making ethylene and vinyl chloride.
Ethane was first isolated by Michael Faraday in 1834. He obtained it by passing electric current through a mixture of hydrochloric acid and ethanol. The name “ethane” comes from the Greek word for ether (ἠθέρ).
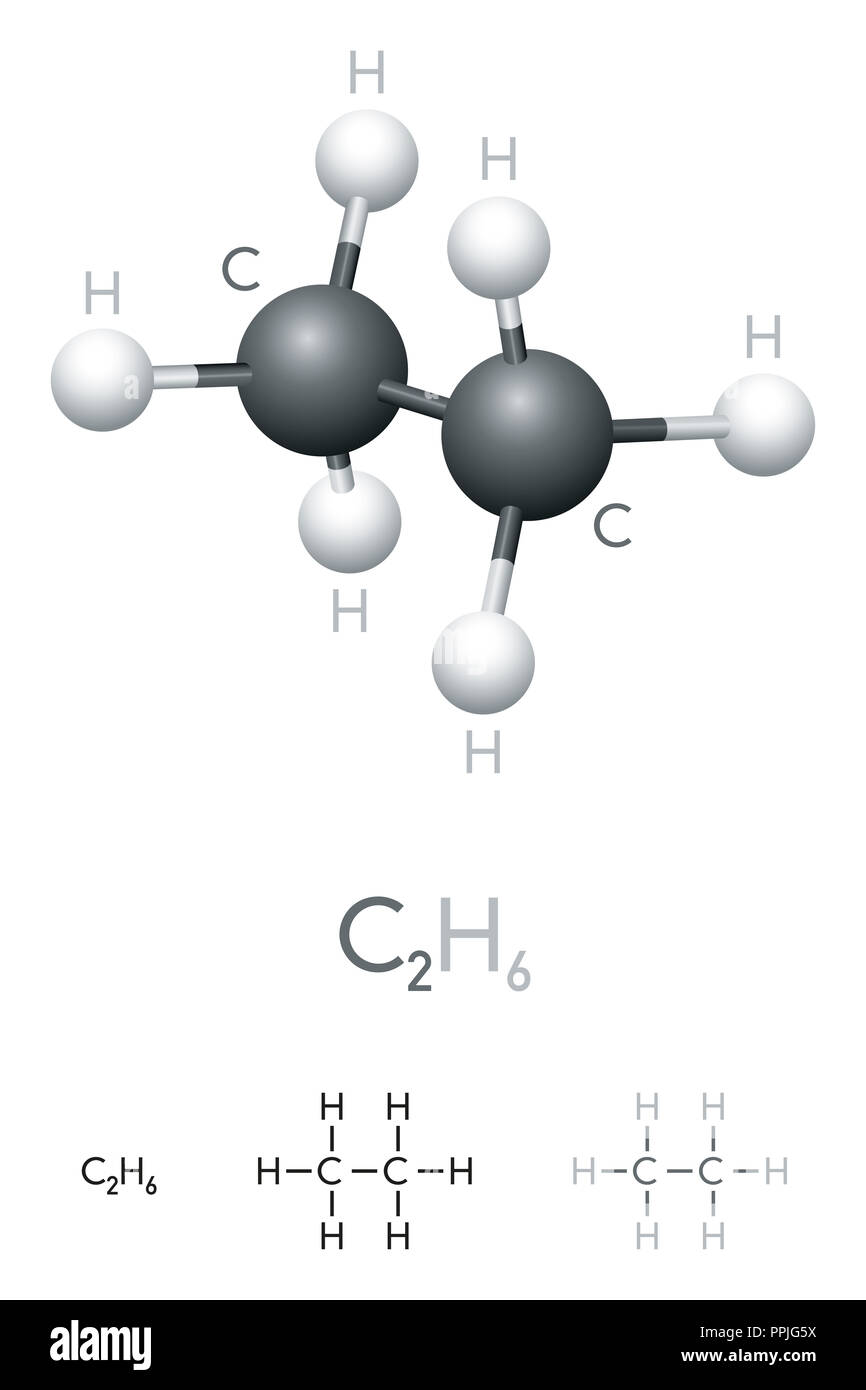
The chemical formula of ethane is C_2H_6. The molecule consists of two carbon atoms bonded together by a single covalent bond, with each carbon atom having three hydrogen atoms bonded to it. Ethane is therefore classified as a saturated hydrocarbon.
The boiling point of ethane is -89°C (-128°F), and the melting point is -183°C (-297°F). The density of ethane at STP (standard temperature and pressure) is 0.554 g/mL.
Ethane is insoluble in water but soluble in most organic solvents. It burns in air to form carbon dioxide and water vapor:
2 C_2H_6 + 7 O_2 → 4 CO_2 + 6 H_2O