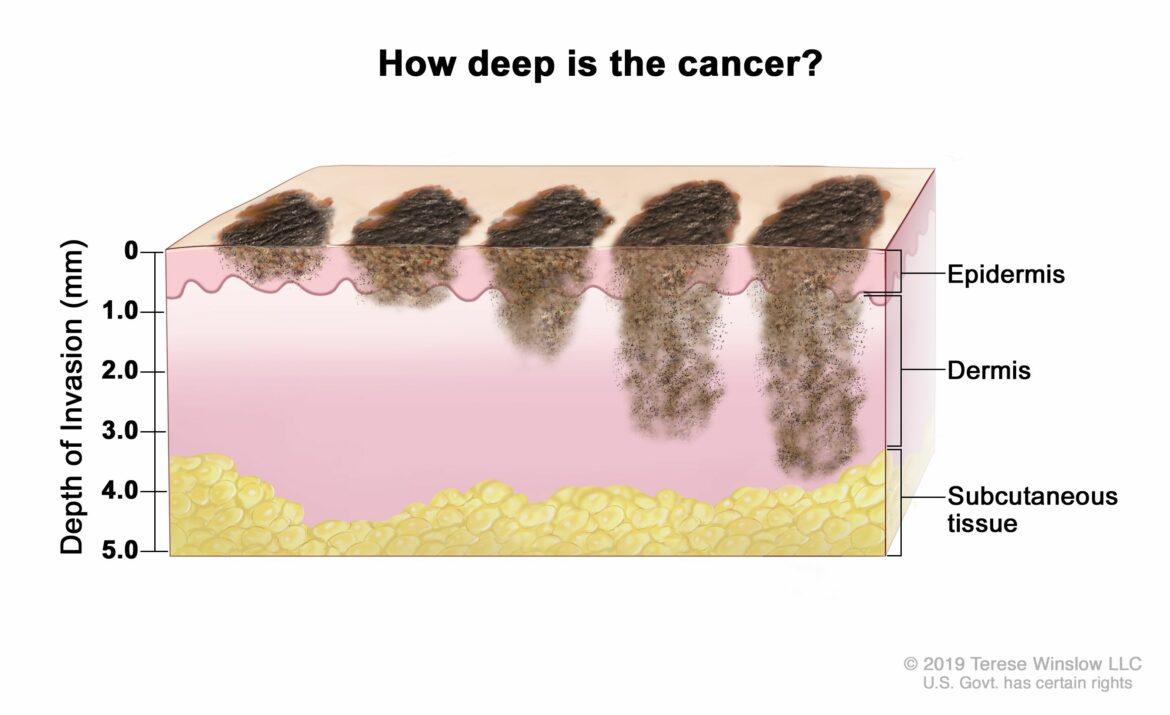
Melanoma is a cancer of the cells that give color to the skin (melanocytes). It is the most serious type of skin cancer. Melanoma can occur anywhere on the body, but it is most likely to develop in areas that have been exposed to sunlight, such as the face, neck, chest, back, shoulders, and legs. Melanoma can also occur on parts of the body that have not been exposed to sunlight.
Most melanomas are black or brown. They can also be pink, red, purple, blue, or white. Melanomas may look like moles or birthmarks. They can be raised above the surface of the skin or flat. Some melanomas have a mixture of colors.
People who have fair skin and who sunburn easily are at greater risk for developing melanoma. People with dark skin are at lower risk for developing melanoma; however, when they do get this disease, it is more likely to be fatal. Other factors that may increase your risk include family history and having had previous melanomas or other types of skin cancer.
If you notice any changes in a mole on your body, see a dermatologist right away so that he or she can check it out. You should also see a dermatologist if you notice any new moles on your body or any changes in existing moles . The earlier melanoma is found and treated , the better chance you have for surviving this disease .
There are three main types of treatment for melanoma: surgery , radiation therapy , and chemotherapy . Surgery is usually the first treatment option if the tumor has not spread to other parts of the body . Radiation therapy uses high-energy waves to kill cancer cells . Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells .
New treatments for metastatic melanoma ( stage 4) include targeted therapies and immunotherapy . Targeted therapy drugs work by targeting specific genes or proteins that help cancer cells grow while immunotherapy drugs work by helping your own immune system fight cancer cells .