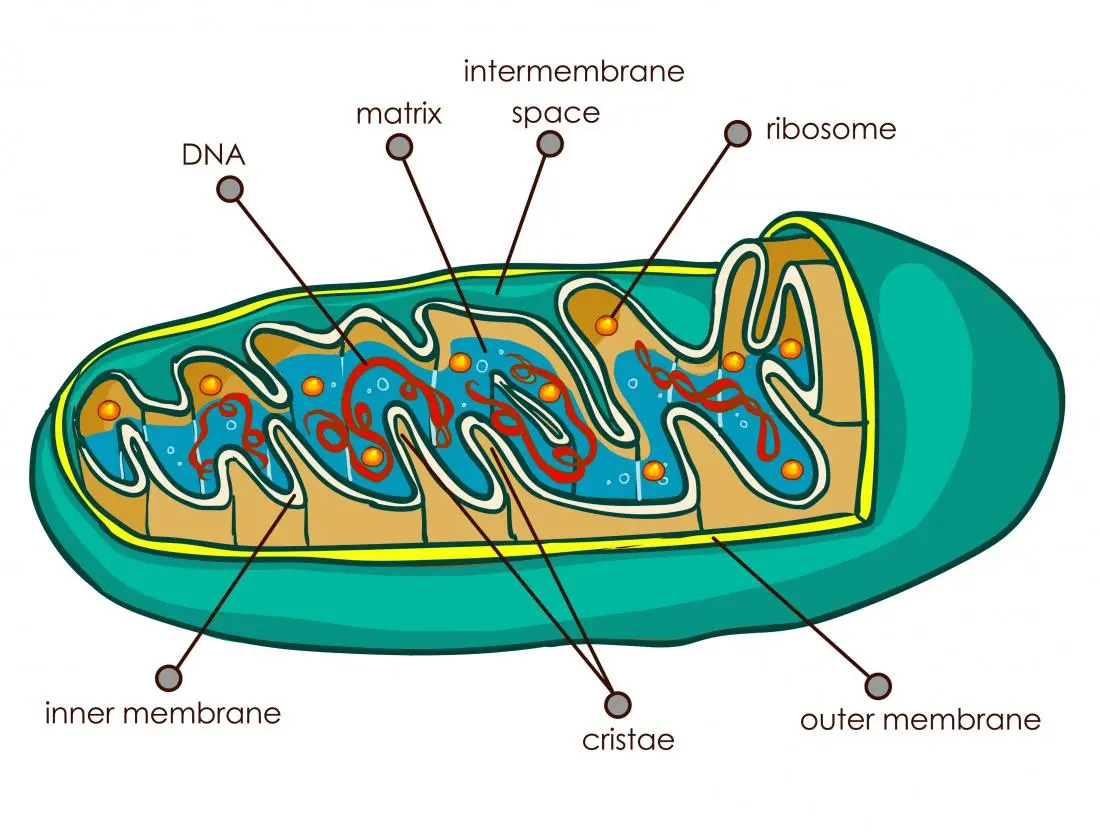
Mitochondria are organelles within cells that are responsible for generating energy in the form of ATP through cellular respiration. Cellular respiration is a process that occurs in the mitochondria, and it consists of three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose to two molecules of pyruvate, and it takes place in the cytoplasm. The Krebs cycle is the second stage of cellular respiration, and it takes place in the matrix of the mitochondrion. In this stage, pyruvate is converted into acetyl-CoA, which then enters into the Krebs cycle. The final stage of cellular respiration is oxidative phosphorylation, which takes place on the inner mitochondrial membrane. In this stage, ATP is produced by using oxygen to oxidize NADH and FADH2.
The mitochondrion has a double membrane structure with an outer membrane and an inner membrane. The space between these two membranes is called the intermembrane space while the space inside the inner membrane is called the matrix. The outer mitochondrial membrane contains porins which are proteins that allow small molecules like oxygen and nutrients to enter into mitochondrion. The inner mitochondrial membrane contains enzymes involved in aerobic metabolism as well as cristae which are folds in this membrane that increase its surface area for better enzyme activity . Cristae also contain most ofthe respiratory chain enzymes involved in oxidative phosphorylation .