Researchers from Politecnico di Milano have formulated a catalyst that can be activated by sunlight, effectively enabling esterification reactions and thereby cutting down on the need for rare metals, paving the way for a more environmentally sustainable approach to chemical synthesis. This remarkable development, highlighted in Nature Synthesis, could play a crucial role in resource conservation and reducing environmental degradation. Acknowledgement: Polytechnic University of Milan
This groundbreaking invention by the Polytechnic University of Milan heralds a new era in sustainable chemical creation, fostering pioneering methods that allow chemicals to be produced in a way that is both efficient and eco-friendly. The details of this research have recently been made public in the journal Nature Synthesis.
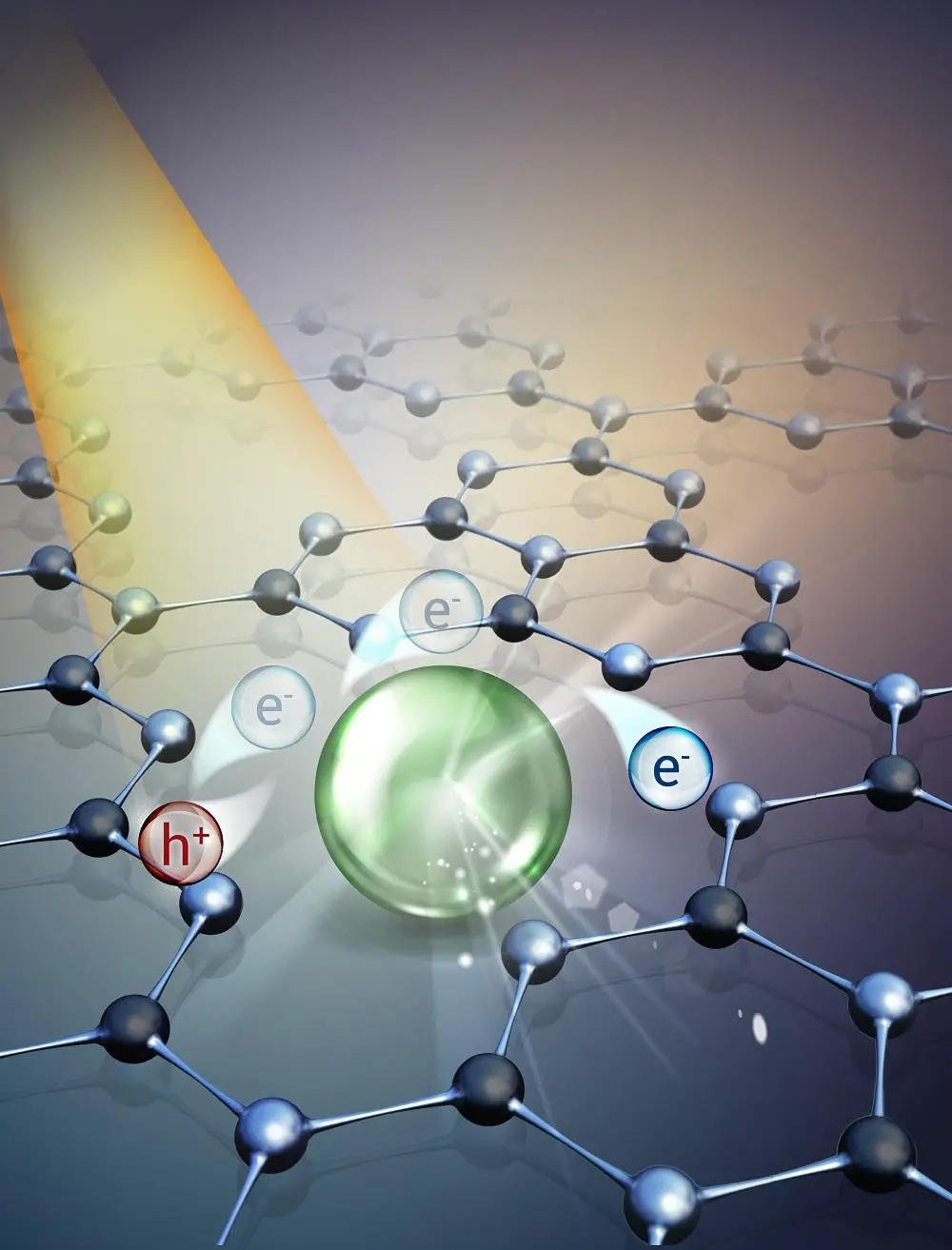
The team achieved this by employing an inventive method of spreading isolated atoms on supports made of carbon nitride, resulting in a catalyst with enhanced activity and selectiveness in esterification reactions. This vital reaction involves the fusion of carboxylic acids and bromides to create products essential in the production of medicines, food additives, and polymers.
What sets this catalyst apart is its ability to minimize the use of rare metals, marking a substantial stride towards preserving vital resources and enhancing the sustainability of processes. Additionally, the catalyst’s activation through sunlight eradicates the necessity for energy-consuming methods. This revelation carries immense potential for decreasing reliance on limited resources and lessening the environmental harm caused by catalytic procedures.
The project was overseen by Professor Gianvito Vilé, an Associate Professor of Chemical Engineering at the ‘Giulio Natta’ Department of Chemistry, Materials, and Chemical Engineering, with Mark Bajada, a Marie Skłodowska-Curie Postdoctoral Fellow at the Polytechnic University of Milan, listed as the primary author of the study. Conducted in conjunction with researchers from the University of Milan Bicocca and the University of Turin, the study received financial support from the European Commission via a Marie Skłodowska-Curie Postdoctoral Fellowship and a recently granted Horizon Europe project to the Polytechnic University of Milan (SusPharma).
Citation: “Light-driven C–O coupling of carboxylic acids and alkyl halides over a Ni single-atom catalyst” by Mark A. Bajada, Giovanni Di Liberto, Sergio Tosoni, Vincenzo Ruta, Lorenzo Mino, Nicolò Allasia, Alessandra Sivo, Gianfranco Pacchioni and Gianvito Vilé, 15 June 2023, Nature Synthesis.
DOI: 10.1038/s44160-023-00341-3
Table of Contents
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Sustainable Catalyst
What is the significance of the discovery by Politecnico di Milano researchers?
The discovery by researchers from Politecnico di Milano involves a sunlight-activated catalyst that drives esterification reactions efficiently. This innovation reduces the reliance on rare metals and promotes more sustainable chemical synthesis methods.
How does the sunlight-activated catalyst work?
The catalyst utilizes the innovative technique of dispersing isolated atoms on carbon nitride supports. This enhances its activity and selectivity in esterification reactions, allowing for the efficient creation of products used in various industries.
What are the benefits of reducing the use of rare metals in chemical synthesis?
Reducing the use of rare metals in chemical synthesis is a significant step toward conserving valuable resources. This approach also helps lower the environmental impact of the synthesis process, contributing to more sustainable and eco-friendly practices.
What applications do esterification reactions have?
Esterification reactions are crucial for producing compounds used in medicine, food additives, and polymers. These reactions play a pivotal role in creating products that are integral to various industries, making them a key focus in chemical research.
Who led the project and contributed to the research?
Professor Gianvito Vilé, an Associate Professor of Chemical Engineering at Politecnico di Milano, coordinated the project. Mark Bajada, a Marie Skłodowska-Curie Postdoctoral Fellow, was the first author of the research paper. Collaboration with researchers from the University of Milan Bicocca and the University of Turin was also instrumental in the study.
What funding supported this research?
The research was funded by the European Commission through a Marie Skłodowska-Curie Postdoctoral Fellowship and a Horizon Europe project awarded to Politecnico di Milano (SusPharma).
Where can I find more information about this discovery?
More details about this discovery can be found in the research paper titled “Light-driven C–O coupling of carboxylic acids and alkyl halides over a Ni single-atom catalyst,” published in Nature Synthesis on June 15, 2023 (DOI: 10.1038/s44160-023-00341-3).
More about Sustainable Catalyst
- Nature Synthesis article
- Polytechnic University of Milan
- European Commission Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions
- Horizon Europe


1 comment
polytechnic uni milan nailed it w/ this sunlight thang! catalyst doin’ its thang, less rare metal mess, eco-win!