Mind-Blowing Stellar Convection Simulations Unveil the Twinkling of Giant Stars
Cutting-edge simulations of stellar convection conducted by scientists from the Flatiron Institute and Northwestern University have revealed the mesmerizing phenomenon behind the twinkling of massive stars. Published in Nature Astronomy, this groundbreaking research offers crucial insights into the internal mechanisms of stars larger than our sun.
The Intrinsic Twinkling of Stars
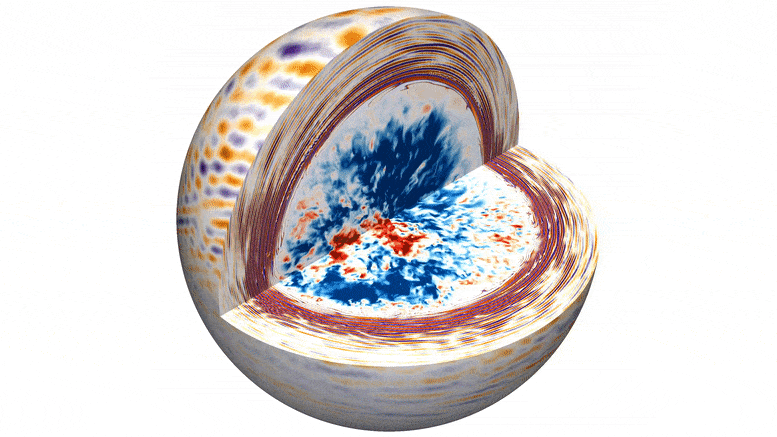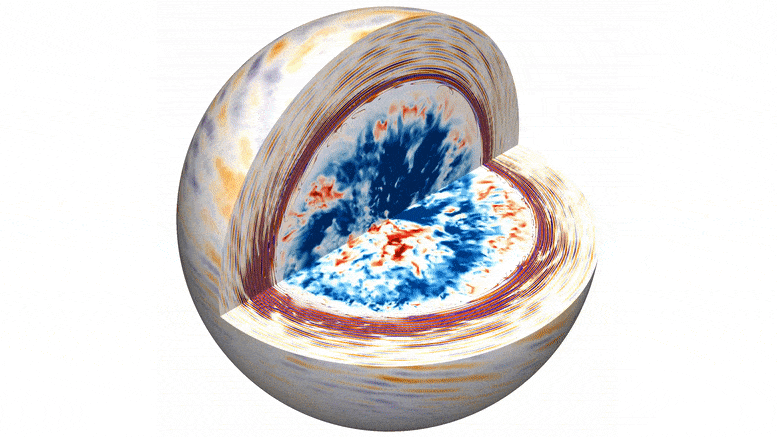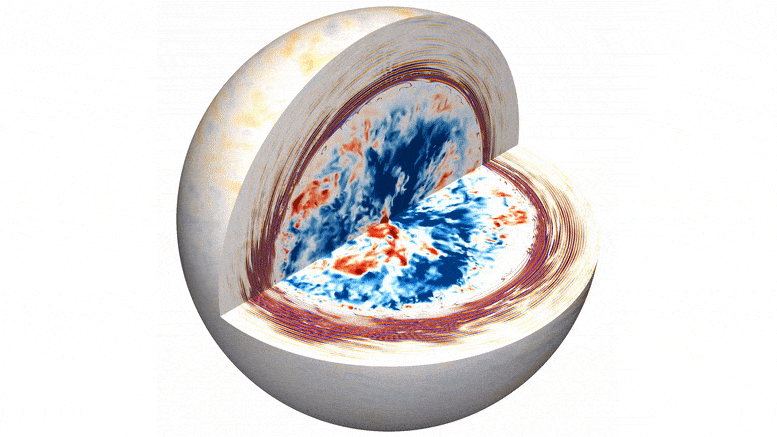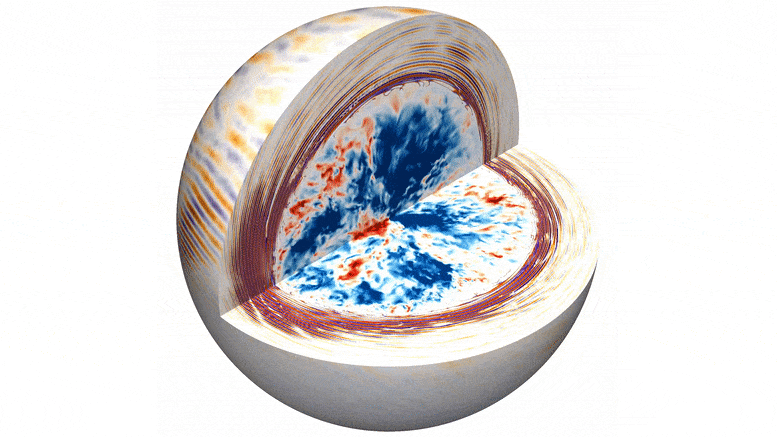
A pioneering team of astrophysicists, led by researchers from the Flatiron Institute and Northwestern University, has developed unprecedented computer simulations that demonstrate how convection deep within a star gives rise to flickering starlight. Unlike the familiar twinkling observed in stars due to Earth’s atmosphere, this flickering arises from the churning processes within a star’s core.
The simulations provide a unique opportunity for astronomers to explore the enigmatic interiors of stars larger than our sun, as reported in the journal Nature Astronomy on July 27.
Understanding the Ripple Effect
The simulations present a vivid 3D visualization of turbulent convection within the core of a massive star, generating waves that ripple outward and cause resonant vibrations near the star’s surface. By studying fluctuations in the star’s brightness caused by these vibrations, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the processes occurring deep within these colossal celestial bodies.
Unlocking the Secrets of Stellar Evolution and Element Creation
Enhanced comprehension of the inner workings of stars will offer valuable insights into star formation, evolution, galaxy assembly, and the creation of heavy elements like the essential oxygen we depend on for life. This newfound knowledge paves the way for future space telescopes to delve into the central regions where stars forge the building blocks of life.
Revisiting the Mystery of ‘Red Noise’
Interestingly, these simulations also shed light on a long-standing stellar mystery known as ‘red noise,’ characterized by unexplained pulsations causing fluctuations in the brightness of hot, massive stars. While core convection was previously suggested as the cause, the simulations indicate that the twinkling resulting from this convection is too faint to account for the observed red noise. This points to other yet-to-be-discovered factors responsible for the phenomenon.
The Challenge of Simulation
Simulating the generation and propagation of these waves in a computer proved to be immensely challenging due to the disparity in timescales. However, the researchers found inspiration from sound waves in music, allowing them to create a filter mimicking a star’s acoustic properties, akin to a sound engineer manipulating audio.
Future Prospects
The research team is further refining their simulations to incorporate additional factors, such as the rapid spinning of massive stars. They are eager to investigate whether fast-spinning stars exhibit flickering induced by core convection detectable by current telescopes.
The findings published in Nature Astronomy with the title “The photometric variability of massive stars due to gravity waves excited by core convection” offer a groundbreaking step toward unraveling the captivating secrets of giant stars and their inner symphony. (DOI: 10.1038/s41550-023-02040-7)
Table of Contents
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Stellar Convection
What did the scientists discover through computer simulations?
The scientists discovered that convection within the cores of massive stars can cause flickering in their light, resulting in twinkling stars.
How could this finding help us understand stars larger than our sun?
By closely observing the twinkling of stars, astronomers may use the simulations to learn more about the internal workings of stars larger than our sun, gaining valuable insights into stellar evolution and element creation.
What is the significance of the red noise observed in hot, massive stars?
Red noise has been a long-standing stellar mystery, causing fluctuations in the brightness of massive stars. While core convection was previously suspected, the simulations suggest it might not be the main cause, leaving room for further exploration of this intriguing phenomenon.
How did the researchers tackle the challenge of simulating wave generation and propagation?
Inspired by sound waves in music, the researchers used a filtering technique to mimic a star’s acoustic properties, helping them accurately simulate the convection-induced waves and resulting starlight fluctuations.
What potential advancements are on the horizon?
The researchers plan to enhance their simulations to include factors like rapid spinning in massive stars, aiming to explore whether fast-spinning stars exhibit detectable flickering induced by core convection using current telescopes.
More about Stellar Convection
- Nature Astronomy: Link
- Flatiron Institute: Link
- Northwestern University: Link
- “The Planets” by Gustav Holst: Link


1 comment
cool, cool, cool! The flickering of stars can teach us sooo much. Can’t wait 4 better telescopes 2 see deeper into stars! #Astronomy