In September 2023, a severe medicane wreaked havoc in northeastern Libya, resulting in widespread flooding and the displacement of numerous residents. Post-disaster satellite imagery illuminated the extent of power outages, particularly affecting the cities of Derna and Al Bayda, where recovery efforts were still underway.
On September 10, 2023, a formidable storm unleashed heavy rainfall across northeastern Libya, leading to significant loss of life and the devastation of coastal cities. Satellite data revealed that in the aftermath of the storm, numerous communities in the region had been plunged into darkness due to power outages.
This powerful storm, akin to a Mediterranean hurricane known as a medicane, brought a staggering 414 millimeters (16 inches) of rainfall to Al Bayda. Meanwhile, the port city of Derna experienced over 100 millimeters (4 inches) of rainfall, far surpassing its average monthly September precipitation of less than 1.5 millimeters (0.1 inches).
Flash floods wreaked havoc, washing away roads and entire neighborhoods, resulting in the displacement of approximately 40,000 people across the country. Preliminary assessments by the United Nations Satellite Center (UNOSAT) indicated that around 10,000 buildings had been damaged by floodwaters, though the full extent of the damage was still being evaluated as of September 22. The destruction of infrastructure also caused widespread power outages, clearly visible in night-time satellite imagery.
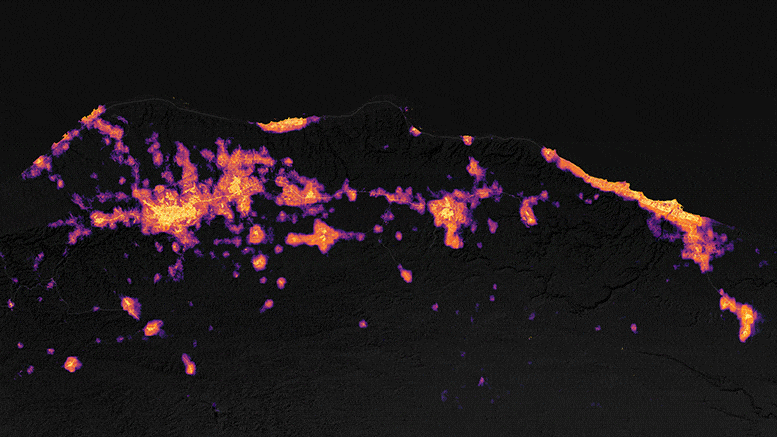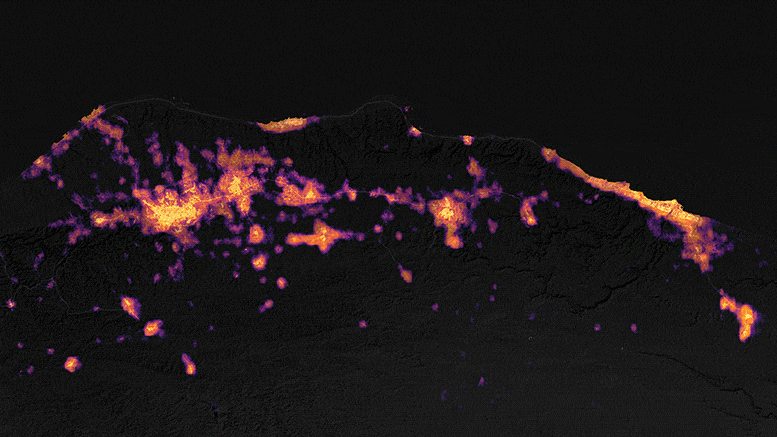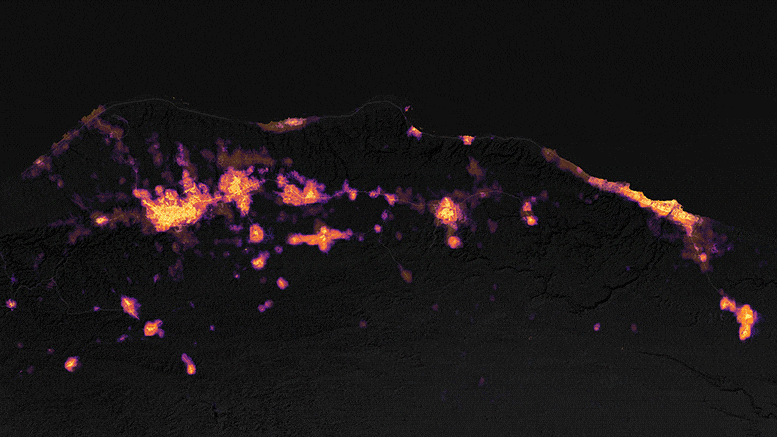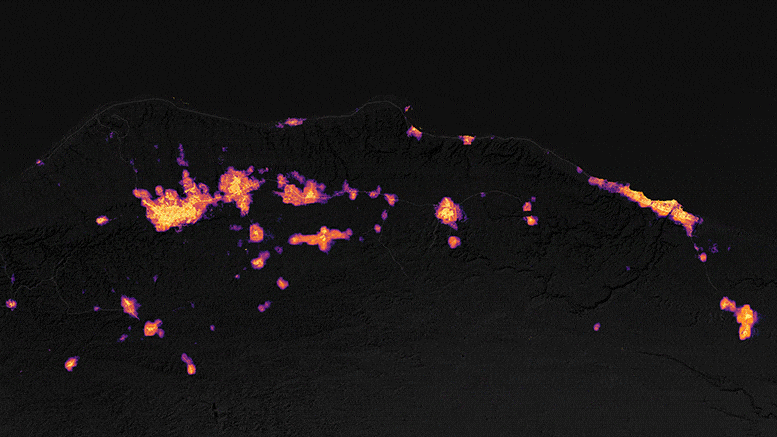
The satellite maps provided illustrate the levels of light emitted by the affected communities in northeastern Libya before and after the catastrophic storm and the peak of torrential flooding. The upper map represents the area on September 8, 2023, while the lower map depicts the same area on September 13, just three days after the storm made landfall.
Ranjay Shrestha, a member of NASA’s Black Marble science team, noted, “There was a significant reduction in power evident in the vicinity of Derna and Al Bayda in the image from September 13 when compared to the baseline image.” These maps were generated from the Black Marble HD dataset, a product provided by Shrestha and Zhuosen Wang, a principal investigator on the science team. The data was collected by the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) sensor on the NASA-NOAA Suomi NPP satellite, with the basemap derived from Landsat 8 and Landsat 9 satellite data.
Derna bore the brunt of the storm’s fury, with flooding leading to the collapse of two dams along a normally dry riverbed (wadi). These dam failures unleashed floodwaters measuring 3 to 7 meters in height, which swept through the city, carrying away roads and buildings into the sea.
The city experienced a noticeable decrease in brightness following the storm. UNOSAT documented these changes in Derna’s luminosity, utilizing Black Marble nighttime light data to assist ground teams in their disaster response efforts.
Some communities near Derna endured up to four days without electricity, as reported by NPR. However, by September 18, 2023, outdoor lighting in Derna was gradually returning to its pre-storm levels. Shrestha remarked, “There’s considerable recovery compared to the September 13 image, although pockets of areas, particularly on the outskirts of the Al Bayda area, are still undergoing restoration.”
It’s important to note that raw, unprocessed images of night lights can be deceptive, as factors such as moonlight, cloud cover, air pollution, snow, seasonal vegetation, and satellite position can influence light reflection. The Black Marble science team meticulously processes the data to account for these variables.
Image credits: NASA Earth Observatory images by Wanmei Liang, utilizing Black Marble data courtesy of Ranjay Shrestha and Zhuosen Wang/NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey, and data from OpenStreetMap.
Table of Contents
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Medicane Impact Libya
What is a “medicane” and how did it impact Libya?
A medicane is a Mediterranean hurricane-like weather system. In September 2023, it brought heavy rain and devastation to northeastern Libya, causing significant flooding and loss of life in coastal cities.
What were the consequences of the medicane in terms of power supply?
The storm led to widespread power outages in northeastern Libya, particularly affecting Derna and Al Bayda. These cities experienced substantial darkness in the aftermath of the storm, as observed in satellite imagery.
How severe was the rainfall during the storm?
The medicane brought a staggering 414 millimeters (16 inches) of rain to Al Bayda and over 100 millimeters (4 inches) to Derna, exceeding the latter’s typical monthly September rainfall of less than 1.5 millimeters (0.1 inches).
What was the extent of the damage caused by the flooding?
Flash floods swept away roads and entire neighborhoods, displacing approximately 40,000 people across Libya. Preliminary assessments suggested that about 10,000 buildings were damaged by floodwater, though further evaluation was ongoing as of September 22.
How did the power outages affect recovery efforts?
Infrastructure damage due to flooding resulted in power outages, impeding recovery efforts. This impact can be clearly seen in satellite images taken at night.
What does the satellite imagery reveal about the changes in light emitted from affected areas?
Satellite maps displayed changes in the amount of light emitted by communities in northeastern Libya before and after the storm. The imagery highlights the significant reduction in brightness in the vicinity of Derna and Al Bayda post-storm.
How long did some communities go without electricity, and what was the recovery progress?
Certain communities near Derna endured up to four days without electricity. By September 18, 2023, outdoor lighting in Derna was gradually returning to pre-storm levels, indicating ongoing recovery efforts.