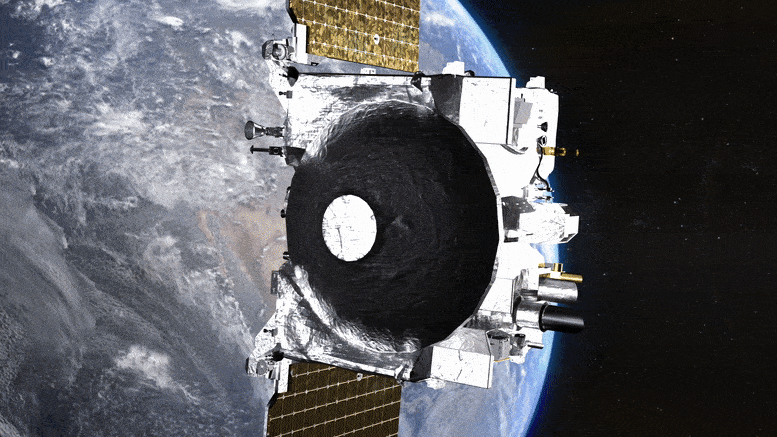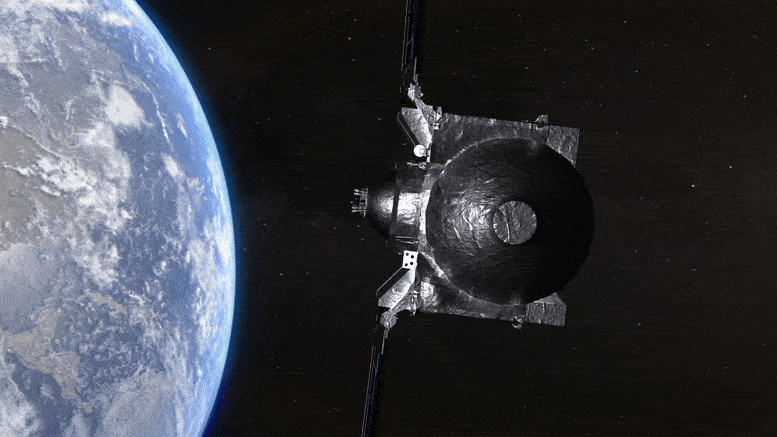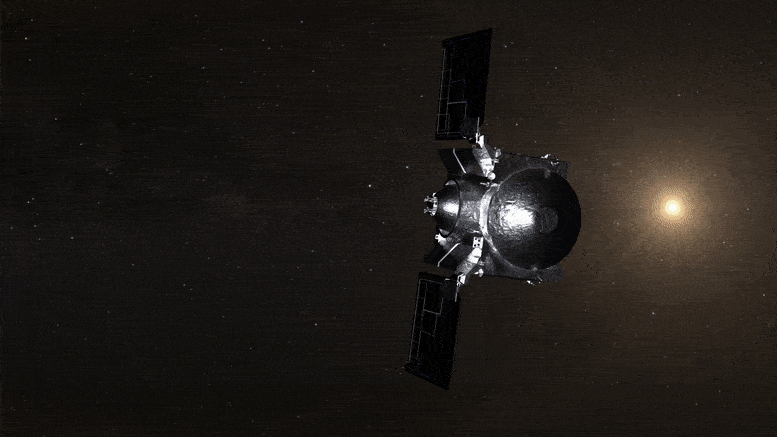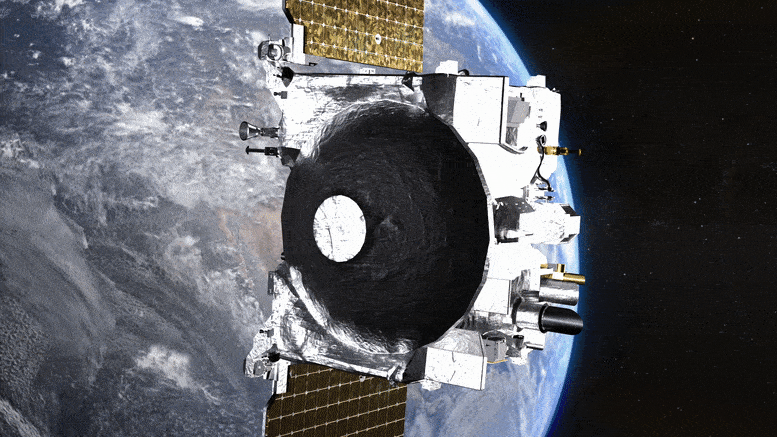
The vessel departs Earth, transitioning to an extended assignment now named OSIRIS-APEX. Acknowledgment: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Conceptual Image Lab
Completing its final assignment for the current mission, NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft discharged its sample capsule back to Earth mere moments ago. Approximately 20 minutes following this event, the spacecraft ignited its thrusters to navigate away from Earth, setting its sights on its new mission objective, asteroid Apophis, and adopting the new designation OSIRIS-APEX.
Measuring approximately 1,000 feet in diameter, Apophis is set to approach Earth to within 20,000 miles—substantially less than one-tenth of the Earth-Moon distance—in the year 2029. After this close passage, OSIRIS-APEX is planned to commence orbiting Apophis to investigate the ramifications of the encounter on the asteroid’s orbital path, rotational velocity, and surface conditions.
Featured is an artist’s rendering of the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft engaging its thrusters in proximity to asteroid Apophis. Acknowledgment: Heather Roper
Table of Contents
Exploring the Extended Mission of OSIRIS-APEX: From Bennu to Apophis
Supervised by NASA, the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft successfully met its core mission of acquiring a sample from asteroid Bennu. However, the exploration continues. Transitioning to its extended phase, the spacecraft adopts its new mission, OSIRIS-APEX.
From Earth Passage to Confronting Apophis
Today, the OSIRIS-REx spacecraft will momentarily traverse our atmosphere, returning its invaluable sample from Bennu. Yet, the exploration is far from complete. Rather than being decommissioned following its terrestrial encounter, the spacecraft is slated for a new undertaking: an in-depth study of the near-Earth asteroid, Apophis, which is on course for a remarkable close pass by Earth in 2029.
On April 13, 2029, the notorious asteroid Apophis will closely approach Earth. At a distance of less than 40,000 km, the celestial body will be perceptible to unaided human vision. Earth’s gravity will significantly affect Apophis during this pass, modifying its trajectory and contributing to the uncertainty of its future orbit. It was formerly considered that this event held a slight possibility of rerouting Apophis into a perilous new orbit, where it could potentially collide with Earth in subsequent solar orbits. Acknowledgment: ESA
Apophis: A Distinctive Member of the Asteroid Population
Initially identified in 2004, Apophis was once thought to present an impact hazard to Earth during its 2029 approach. However, follow-up observations have largely dismissed this threat, although the event still holds notable significance. The close pass will be one of the nearest approaches by an asteroid of this scale. Observers in Europe and Africa will be uniquely positioned to view this celestial occurrence without telescopic aid.
Aims of the OSIRIS-APEX Mission
Initially launched in 2016, OSIRIS-REx’s primary mission aimed to furnish scientists with insights into the formation of the solar system and Earth’s habitability through sample collection from Bennu. As for OSIRIS-APEX, while there is no plan to secure a sample from Apophis, the mission will focus on extensive 18-month observations of the asteroid. The spacecraft will move in close proximity to the asteroid’s surface and engage its thrusters, revealing the subterranean layer and thereby allowing scientists to scrutinize Apophis’s material composition.
Furthermore, the mission endeavors to understand the influence of Earth’s gravitational forces on Apophis during its 2029 close pass and to distinguish its material composition from that of Bennu.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about OSIRIS-APEX Mission
What is the new mission of NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft?
The new mission for NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft is called OSIRIS-APEX. After successfully completing its primary mission of collecting a sample from asteroid Bennu, the spacecraft will now focus on extensive observations of another near-Earth asteroid, Apophis.
When is asteroid Apophis expected to closely approach Earth?
Asteroid Apophis is expected to make a close approach to Earth on April 13, 2029. It will come within 20,000 miles of Earth, which is less than one-tenth the distance between Earth and the Moon.
What are the objectives of the OSIRIS-APEX mission?
The OSIRIS-APEX mission aims to study the material properties of asteroid Apophis and to understand the effects of Earth’s gravitational forces on its orbit during its 2029 close approach. While there is no intent to collect a sample from Apophis, the spacecraft will carry out in-depth observations for 18 months.
How close will Apophis come to Earth in the year 2029?
In the year 2029, Apophis will approach Earth at a distance of less than 20,000 miles, which is substantially less than one-tenth of the distance between Earth and the Moon.
Was Apophis ever considered a threat to Earth?
Initially discovered in 2004, Apophis was once deemed to potentially pose an impact threat during its 2029 close approach. However, subsequent observations have largely mitigated these concerns, although the close pass remains significant.
What was the primary mission of OSIRIS-REx before transitioning to OSIRIS-APEX?
Before transitioning to OSIRIS-APEX, the primary mission of OSIRIS-REx was to collect a sample from asteroid Bennu. The objective was to aid scientists in understanding the solar system’s formation and Earth’s habitability.
Will residents of specific regions be able to observe Apophis with the naked eye?
Yes, during its 2029 close approach, Apophis will be visible to the naked eye for observers located in Europe and Africa.
What is the duration of the OSIRIS-APEX mission?
The OSIRIS-APEX mission is planned to last for 18 months, during which the spacecraft will perform extensive observations of asteroid Apophis.
More about OSIRIS-APEX Mission
- NASA’s Official Page on OSIRIS-REx
- Goddard Space Flight Center Conceptual Image Lab
- European Space Agency (ESA) Information on Apophis
- OSIRIS-REx Mission Objectives
- Details on Apophis’ Close Approach in 2029
- Scientific Objectives of Studying Asteroids
- Asteroid Bennu Sampling Mission
- The Solar System’s Formation and Earth’s Habitability