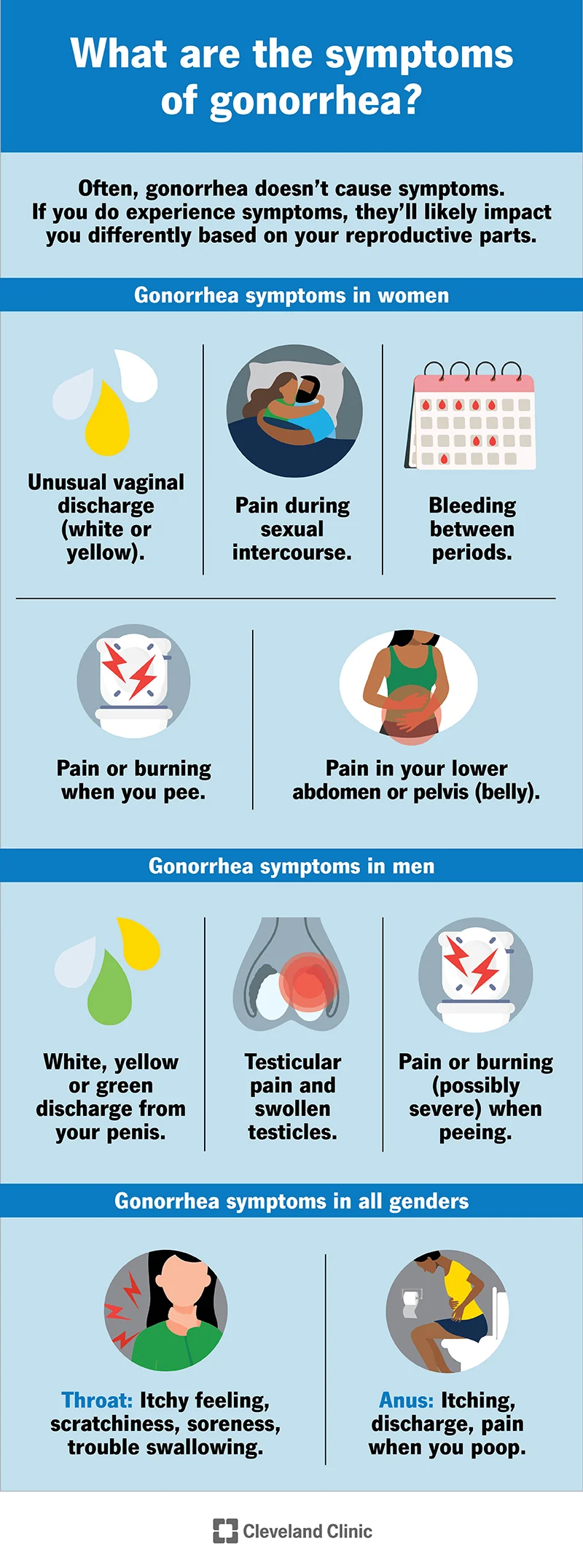
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infection with this bacterium can cause inflammation of the urethra (urethritis), cervix (cervicitis), anus (proctitis), rectum (rectal gonorrhea), and pharynx (throat gonorrhea). Gonorrhea can also infect the eyes and, rarely, the joints. The incubation period for gonorrhea is 2 to 14 days.
left untreated, gonorrhea can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease in women, which can lead to infertility. In men, untreated gonorrhea can lead to epididymitis, which can lead to infertility. Gonorrhea can also be passed from a mother to her baby during childbirth, causing neonatal conjunctivitis or neonatal pneumonia.
Gonococcal infections are usually diagnosed by testing a sample of discharge from the infected site for the presence of N. gonorrhoeae bacteria. Treatment for gonorrhea typically involves antibiotics; however, antibiotic resistance is on the rise globally and has led to treatment failures in some cases. Prevention of gonococcal infections includes using condoms during sexual intercourse and avoiding contact with infected individuals.