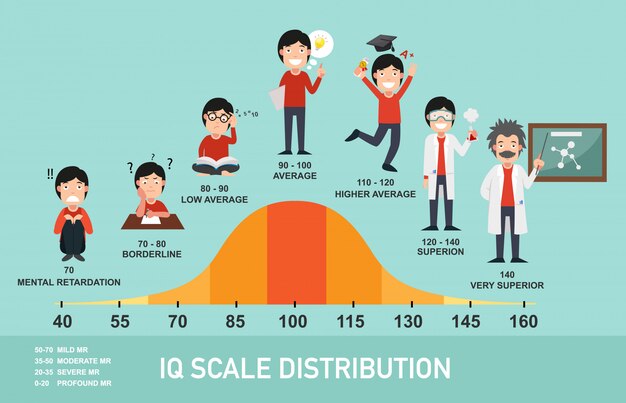
Intelligence quotient (IQ) is a measure of human cognitive ability. It is determined by administering an intelligence test to a group of people and calculating the average score. The average IQ score is 100, with scores above and below this representing higher and lower levels of intelligence, respectively.
IQ tests are used in a variety of settings, including educational, employment, and clinical settings. They can be used to identify giftedness or intellectual disability, as well as to assess the cognitive abilities of individuals for research purposes. Intelligence testing has a long history, with the first intelligence test being developed in 1905.
The most commonly used IQ test is the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS), which consists of verbal and performance subtests. The WAIS has been revised several times since its inception, with the most recent revision being released in 2012. Other popular intelligence tests include the Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale and the Universal Nonverbal Intelligence Test.
Intelligence testing is not without controversy, with some critics arguing that IQ tests are culturally biased and do not accurately reflect an individual’s true intelligence level. However, research has shown that IQ scores are predictive of important life outcomes such as educational attainment and job performance, making them valuable tools for both individuals and organizations alike.