Soluble is a term used in chemistry to describe a substance that can be dissolved in another substance. The term is also used in biology and medicine to describe a protein that can be dissolved in water. Soluble proteins are important for many biological processes, including cell signaling, metabolism, and transportation.
Water is the most common solvent, but other solvents include alcohols, oils, and acids. When a substance is soluble in another substance, it means that the molecules of the first substance are able to mix with the molecules of the second substance. This mixing allows the two substances to interact with each other on a molecular level.
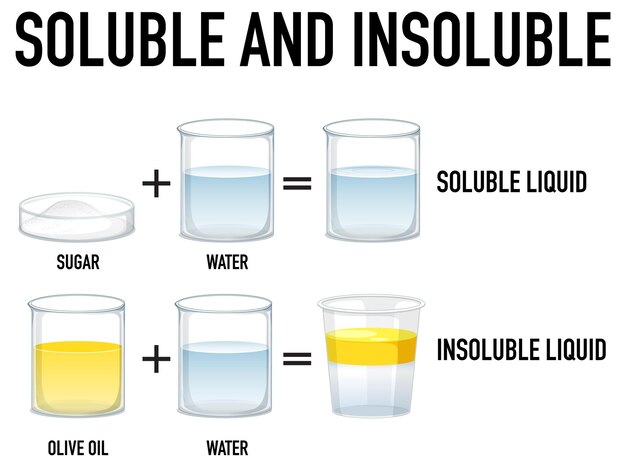
The ability of a substance to dissolve in another substance is called solubility. The degree of solubility depends on the nature of the two substances involved and on the conditions under which they are mixed. For example, salt (sodium chloride) is very soluble in water but not in oil. Sugar is soluble in both water and oil.
The terms “insoluble” and “ insoluble” refer to substances that cannot be dissolved in a given solvent under specified conditions. For example, iron metal is insoluble in water but soluble in acid. The opposite of “soluble” is “ insoluble” .