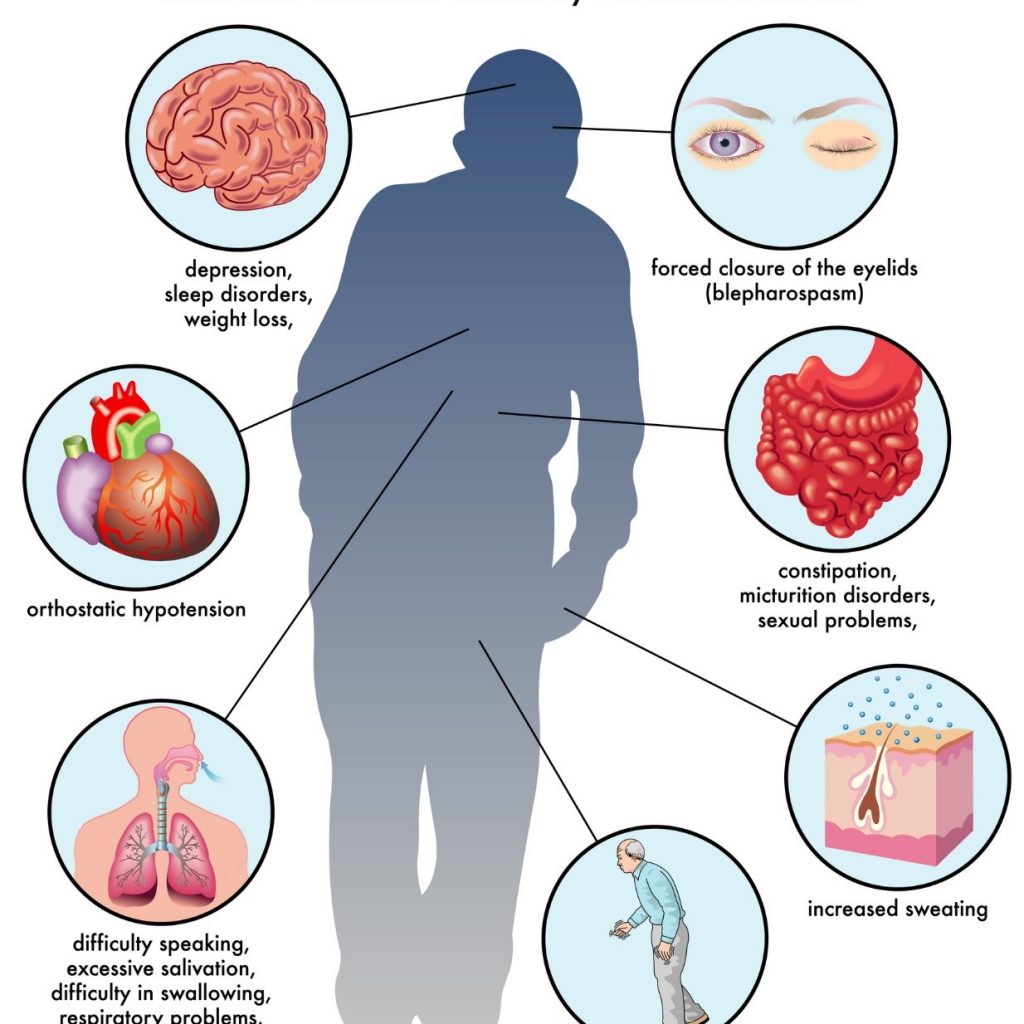
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms generally come on slowly over time. Early in the disease, the most obvious are shaking, rigidity, slowness of movement, and difficulty with walking. Thinking and behavior may also be affected. Dementia becomes common in the advanced stages of the disease. Those with PD are at greater risk of falling and bone fractures.
The cause is unknown but believed to involve both genetic and environmental factors. About 10% of cases are due to known genetic causes such as mutations in genes encoding α-synuclein or leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2). Parkinson’s is usually diagnosed based on a combination of symptoms, medical history, neurological examination, and imaging tests such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). There is no cure for PD, but medications can help improve symptoms. Surgery may be an option in some cases when other treatments have not been effective. The main goal of treatment is to improve quality of life by managing motor and non-motor symptoms.